Bringing Ancient Egypt to Life with XR: Transforming Museum Experiences
By bridging digital and physical realms, museums can enhance learning, spark curiosity, and provide unforgettable educational experiences.

Imagine standing before the Sphinx, exploring its ancient secrets as it transforms vividly before your eyes, right from within a museum gallery. Thanks to innovative uses of Extended Reality (XR), this isn't just imagination—it's an engaging educational reality, as demonstrated by recent pioneering work at the Harvard Museum of the Ancient Near East.
A study by Sara E. Zaia, Katherine E. Rose, and Andrew S. Majewski reveals how integrating virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) into museum outreach significantly enhances visitor engagement and educational impact. The research emphasizes how XR technology breathes new life into traditional museum experiences, deepening visitor understanding and curiosity about archaeological artifacts.
A New Dimension of Learning
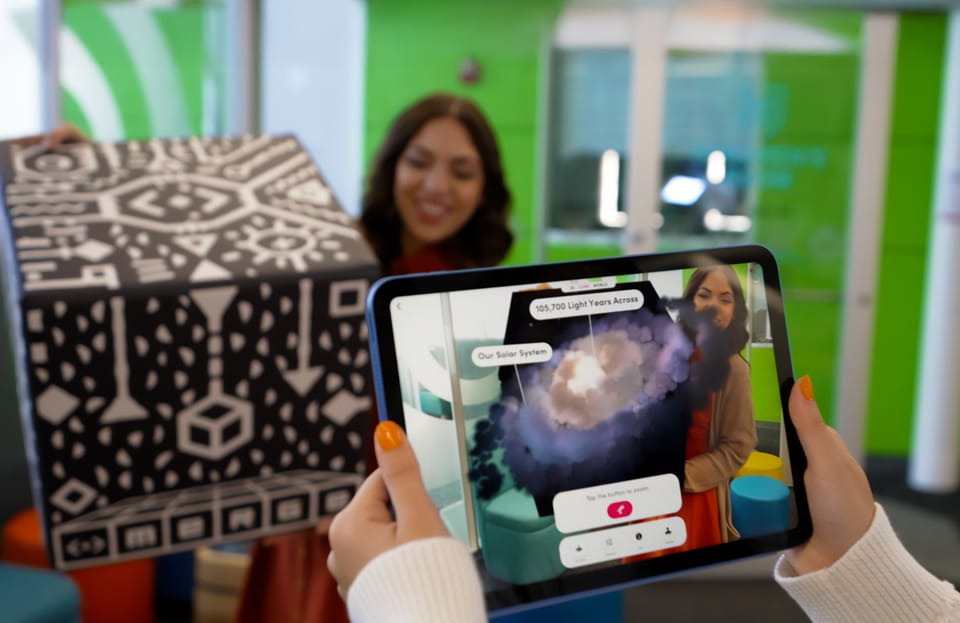
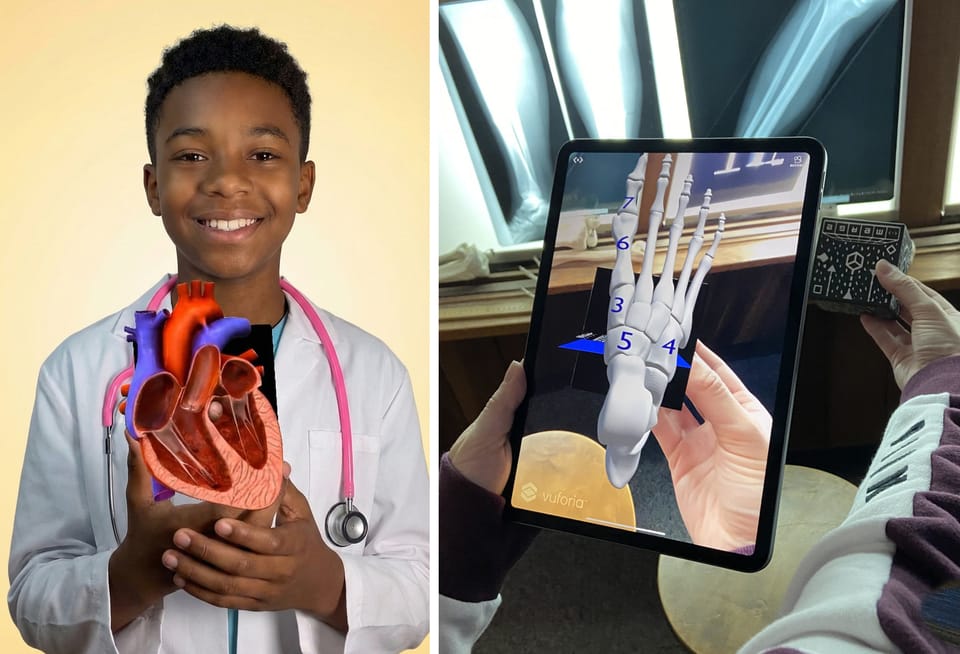
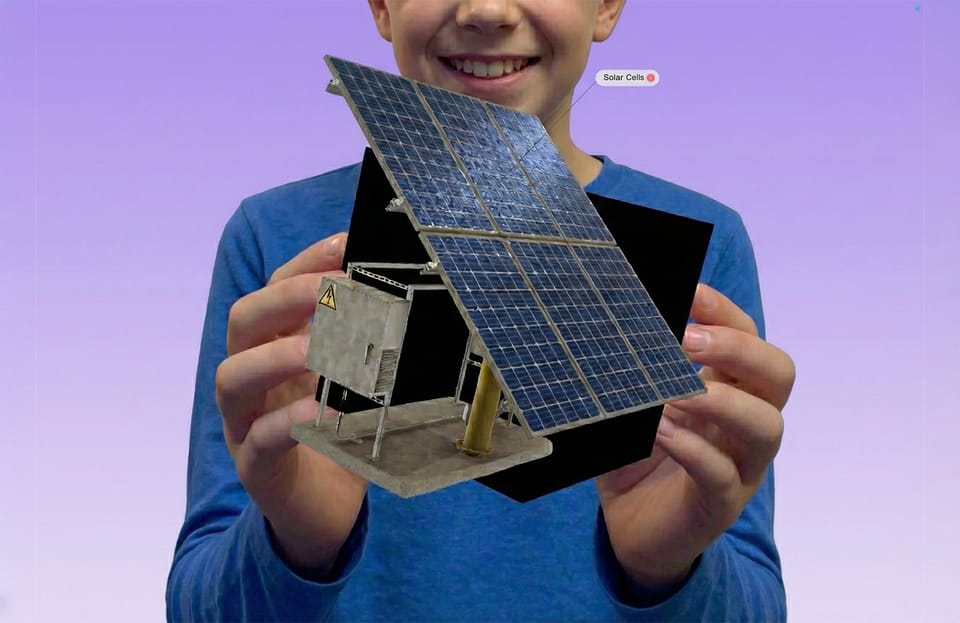
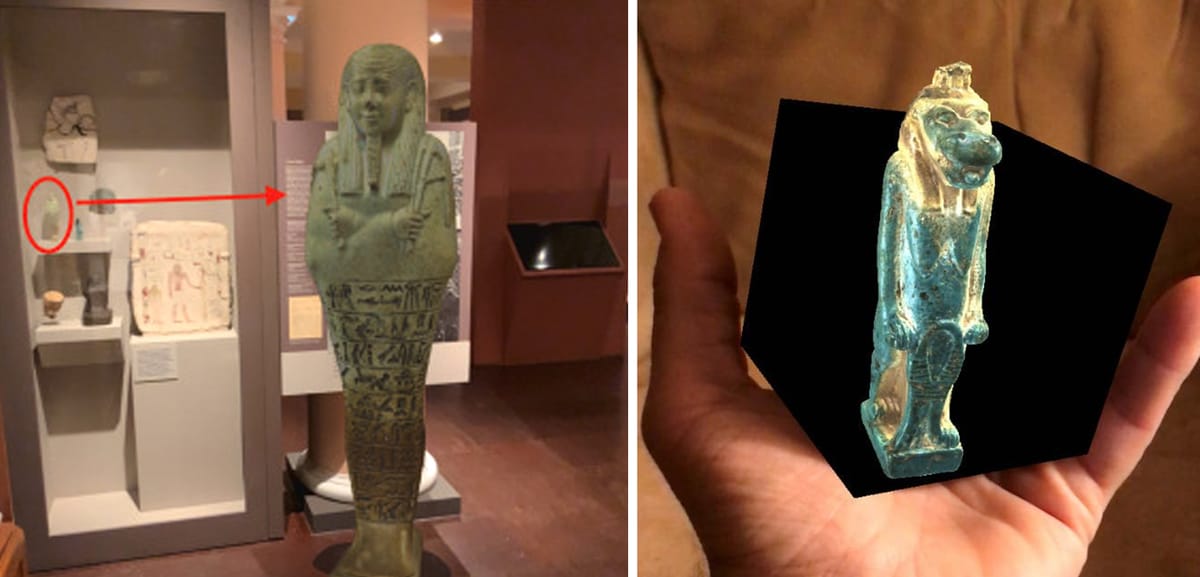
Harvard’s "Amazing Archaeology Fair" showcased XR technology by providing visitors with interactive, immersive experiences featuring Egyptian archaeological artifacts. One standout example involved an AR application that allowed visitors to interact with a 3D model of the Egyptian goddess Taweret. Using the Merge Cube, visitors could virtually manipulate the object, gaining a tactile and visual understanding previously inaccessible behind museum glass.
This technology not only heightened visitors' curiosity about the artifact but encouraged them to engage directly with its physical counterpart within the gallery. Rather than detracting from traditional museum displays, XR tools complemented and enriched them, inspiring deeper inquiry and learning.
Immersion and Interaction
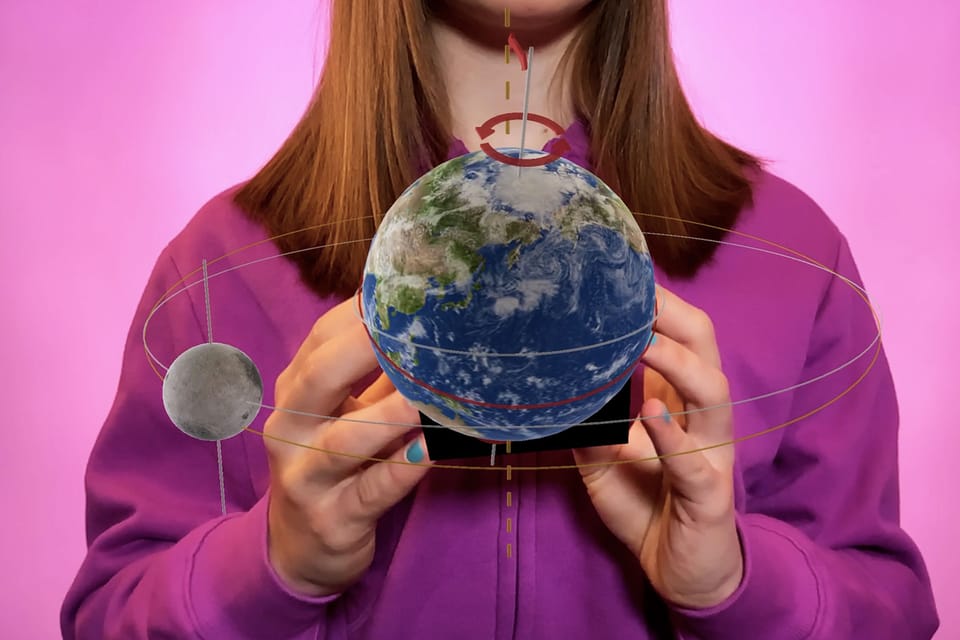
The XR experience does not merely replicate traditional object-based learning—it enhances it by providing visitors a multidimensional interaction. The virtual environment creates a sense of immersion, allowing visitors to "walk around" and explore digital reconstructions as if they were physically present, turning passive viewing into active exploration.
In addition, XR provides emotional resonance, as visitors report feeling more connected to artifacts after interactive digital experiences, aligning closely with the tangible, multi-sensory learning philosophy at the heart of the education approach from Merge EDU.

Overcoming Barriers and Broadening Access
One remarkable benefit of XR is the removal of physical and geographical barriers. Museums that adopt this technology can extend their reach, offering remote, interactive museum experiences to global audiences. Harvard's initiative also demonstrates how XR experiences can be effectively managed and facilitated, overcoming potential hurdles such as technological familiarity and access.

Practical Considerations and Future Implications
While XR technologies bring substantial benefits, researchers caution institutions about the practical challenges, such as staff training, device maintenance, and consistent technological updates. However, the educational advantages significantly outweigh these barriers. As technology becomes increasingly affordable and user-friendly, XR's integration into educational environments like museums is set to expand dramatically.
Looking Ahead
The successful integration of XR technologies at Harvard’s Museum of the Ancient Near East highlights the immense potential of these tools to revolutionize museum education. By bridging digital and physical realms, museums can enhance learning, spark curiosity, and provide unforgettable educational experiences.
Explore how Merge EDU can enhance your educational experiences and inspire a deeper connection with historical artifacts by signing up for a free trial today: TryMerge.com.