A Merge Cube Study: Embodied Learning of Science Concepts Through Augmented Reality Technology
The study's findings clearly indicate that incorporating AR into science education through embodied learning can substantially enhance student engagement, understanding, and collaboration.

Imagine students actively exploring the solar system by physically moving around virtual planets or using their hands to manipulate virtual objects. This isn't a glimpse into a distant future—this immersive learning experience is happening right now through augmented reality (AR) and Merge EDU, transforming how science is taught and experienced.
A groundbreaking study led by Nasser Mansour, Ceren Aras, Judith Kleine Staarman, and Sarah Bader Mohsen Alotaibi demonstrates how AR significantly enhances embodied learning in primary science classrooms, fostering deeper comprehension and collaborative inquiry.
What is Embodied Learning?
Embodied learning integrates physical movement and sensory experiences directly into educational activities, rooting abstract concepts in tangible experiences. When paired with AR technology, like Merge Cube and interactive applications, this educational approach profoundly improves students' understanding of complex scientific concepts.
Learning Through Movement
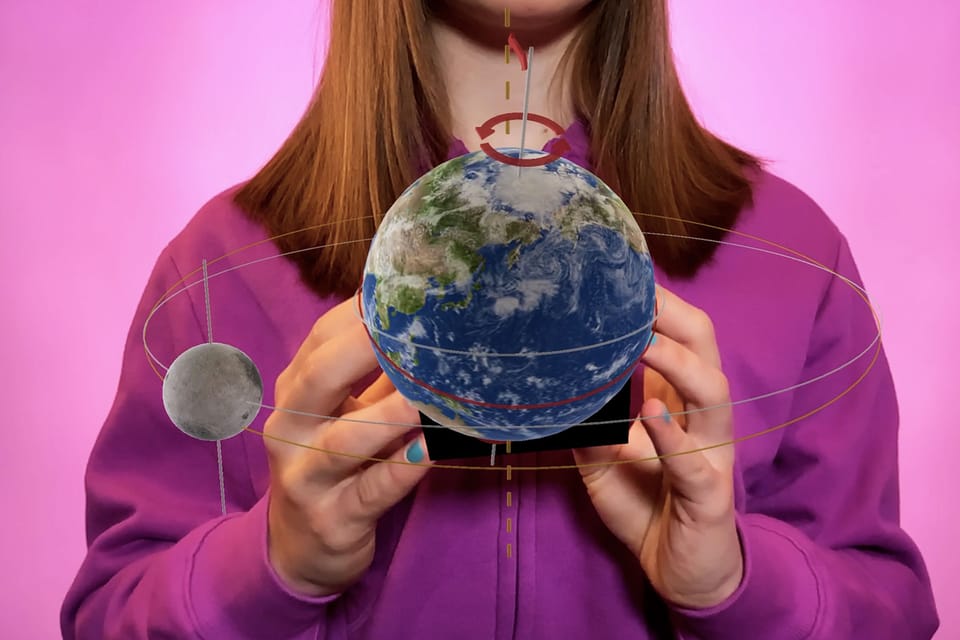
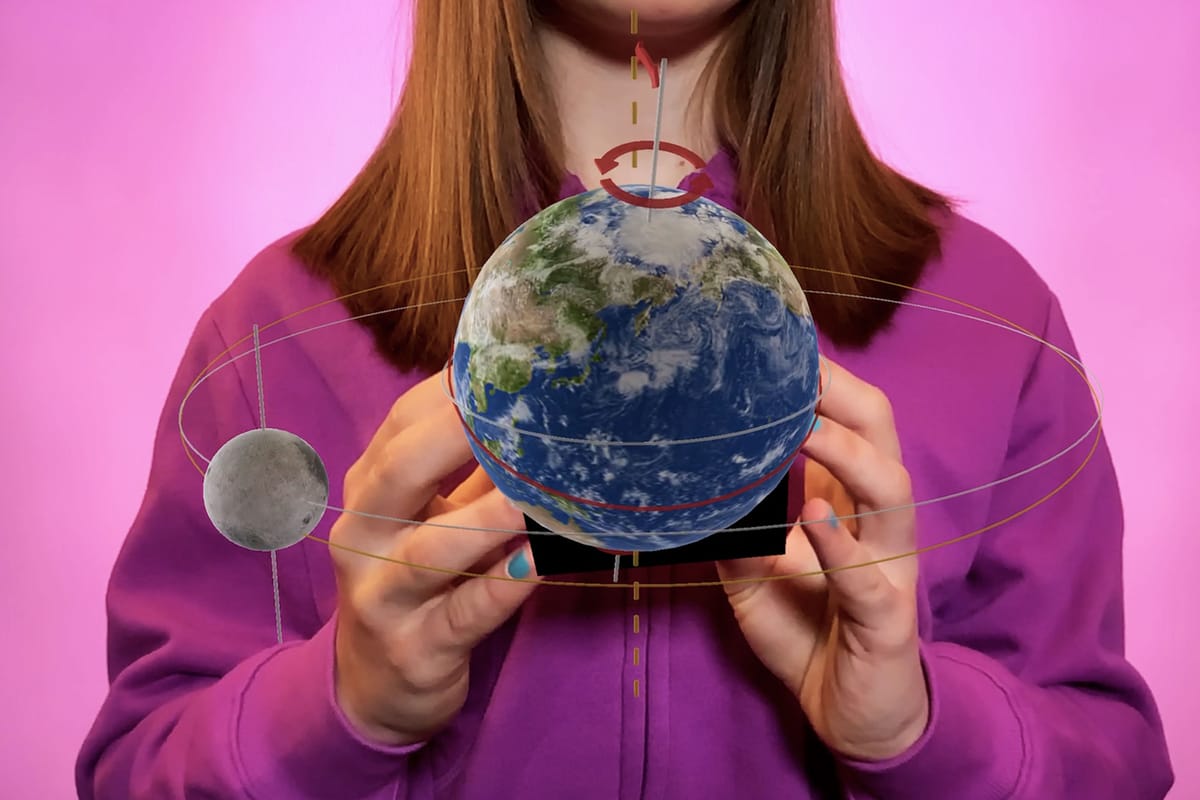
In the study, fifth-grade students in England used AR technology to engage with topics like Earth's rotation and lunar phases. Unlike traditional lessons with static images or videos, students physically interacted with 3D virtual objects via Merge Cube, moving around and manipulating virtual planets with their hands. This active engagement transformed the learning process from passive observation to dynamic exploration.
Students reported that physical interaction with AR made abstract concepts much clearer. They felt empowered to explore, manipulate, and discuss scientific phenomena collaboratively, significantly enhancing their understanding.

Collaboration Enhanced by AR
The collaborative aspect was notably enriched by AR, as students could visually demonstrate their ideas using shared virtual objects. These virtual reference points created vibrant discussions and debates, fostering deeper cognitive and social engagement.
Through AR, students corrected each other’s misconceptions, built collective knowledge, and engaged in peer teaching, creating an inclusive and interactive learning environment. The embodied interactions facilitated by AR encouraged active participation, mutual learning, and clearer communication.
AR and Cognitive Engagement
AR uniquely blends digital and physical experiences, allowing students to learn through movement and gestures, which research shows can greatly improve retention and comprehension. By physically exploring and interacting with scientific models, students develop a profound, intuitive understanding of scientific principles, mirroring authentic scientific inquiry processes.

Implications for the Future of Education
The study's findings clearly indicate that incorporating AR into science education through embodied learning can substantially enhance student engagement, understanding, and collaboration. With the accessible AR tools by Merge, educators can help transform their classrooms into vibrant spaces of exploration and innovation, equipping students with essential skills for the 21st century.
Ready to explore how AR can transform your science classroom? Sign up for the free trial at trymerge.com and print a Merge Paper Cube for your students at MergeCube.com/paper.