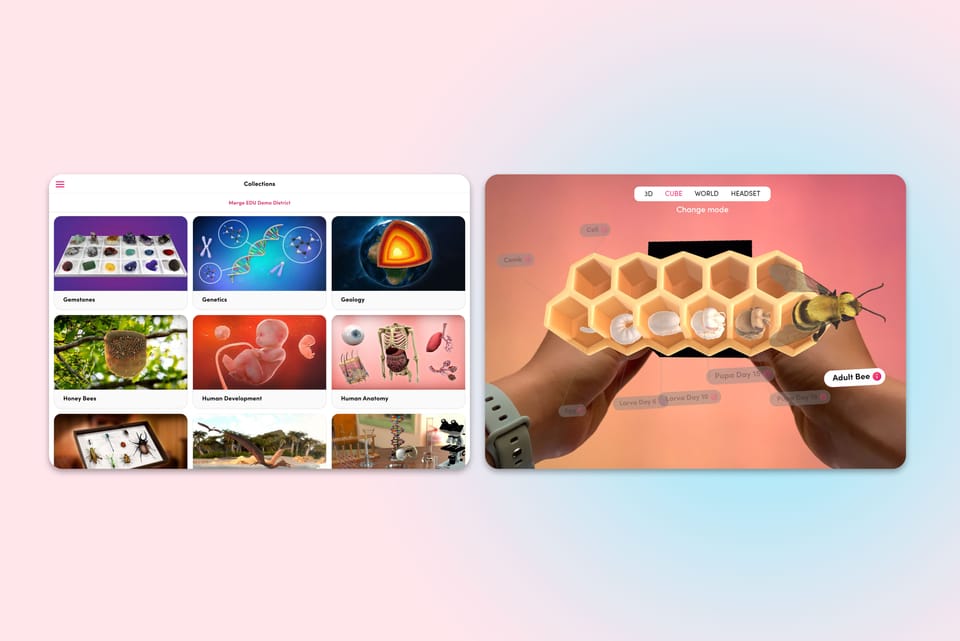
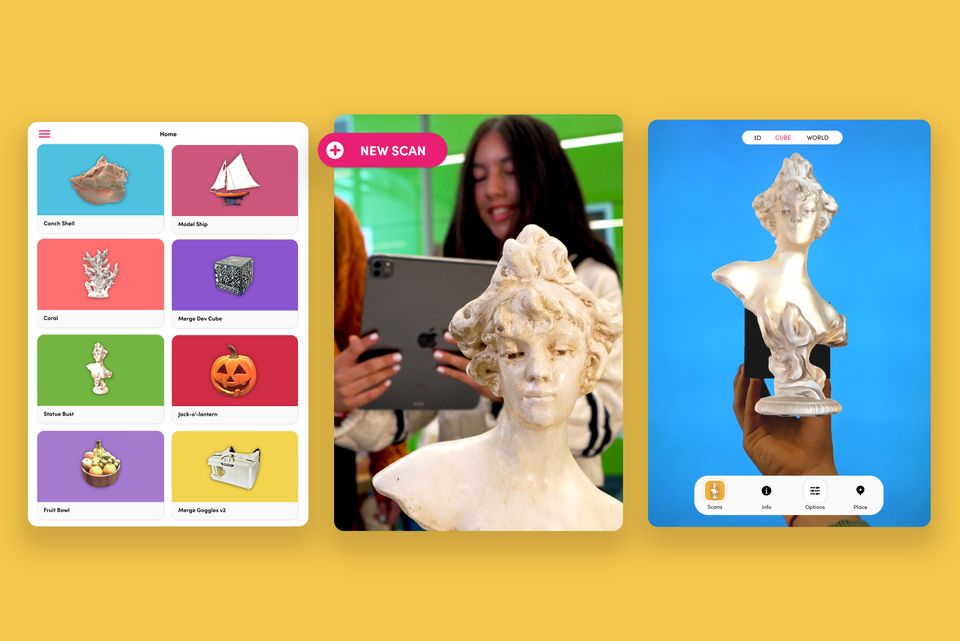
Add Augmented Reality to your Earth Day Lessons with Merge EDU
Earth Day is just around the corner, and there are so many topics in Merge EDU that are perfect for students to learn about on this special day!

Designed to bring interactive, hands-on learning to students using augmented reality (AR) technology, Merge EDU offers countless opportunities to explore, learn, and further develop their understanding of our beautiful planet.
"Look deep into nature, and then you will understand everything better."
- Albert Einstein
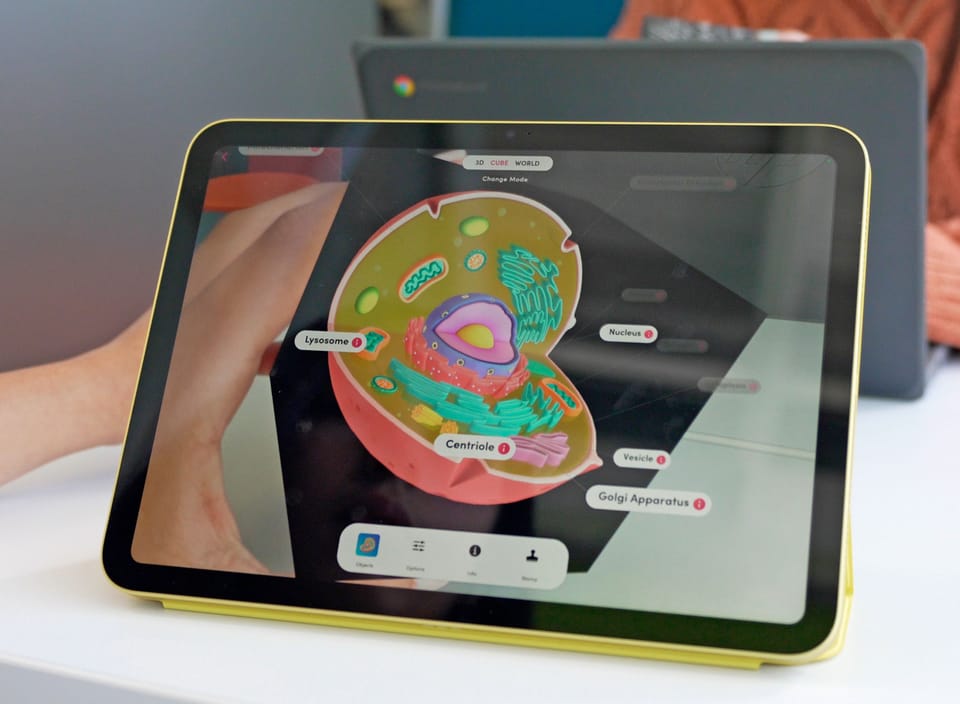
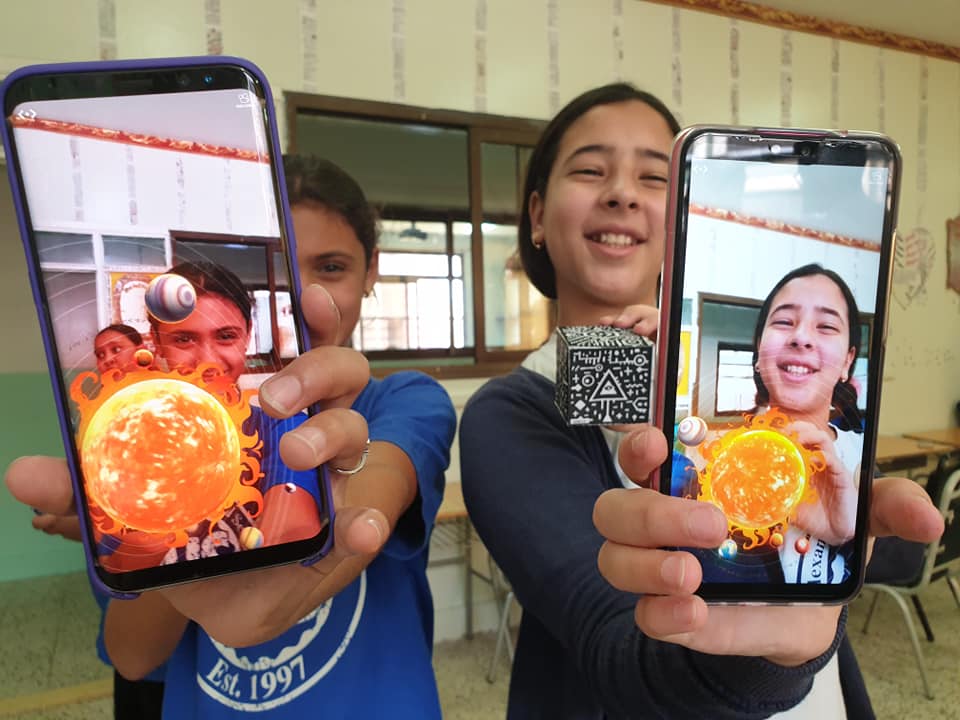
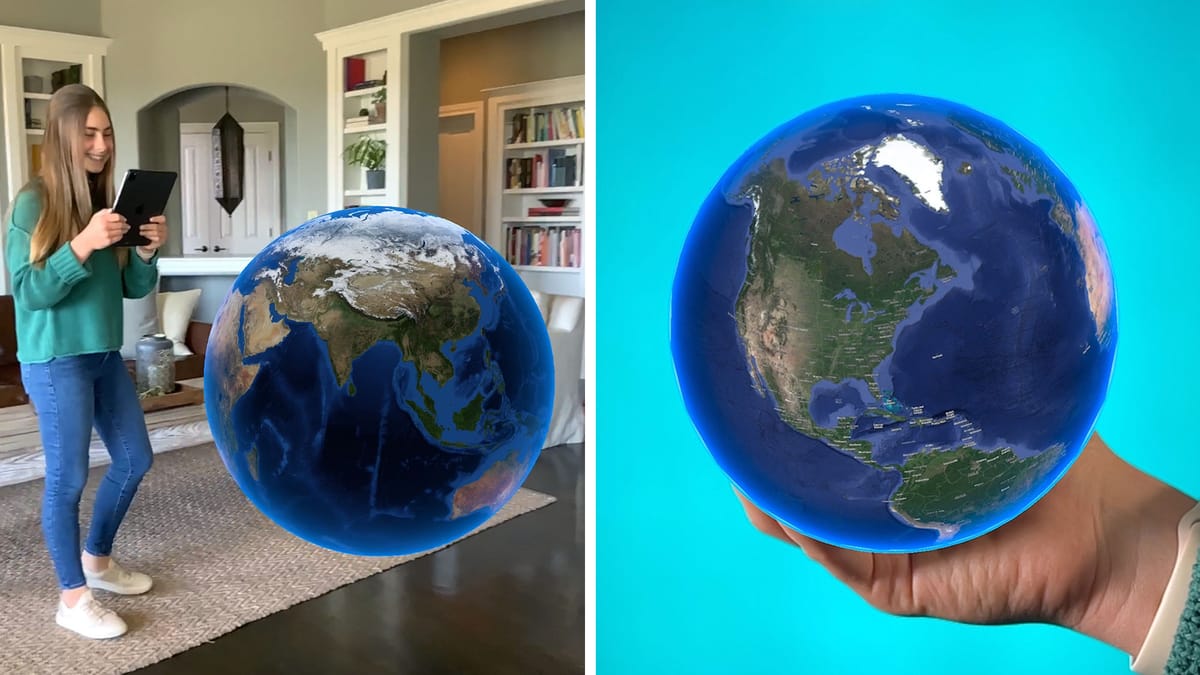
With the Merge Cube, students can physically rotate and examine 3D models of the Earth, its layers, ecosystems, and more. Let's take a look at some of the ways your science class can use Merge EDU to learn more about the earth.

Earth from the Inside
With Merge EDU you can explore geological structures like tectonic plates, layers of the earth, volcanoes, fossils, and rock formations to learn about earth’s physical structure and processes.
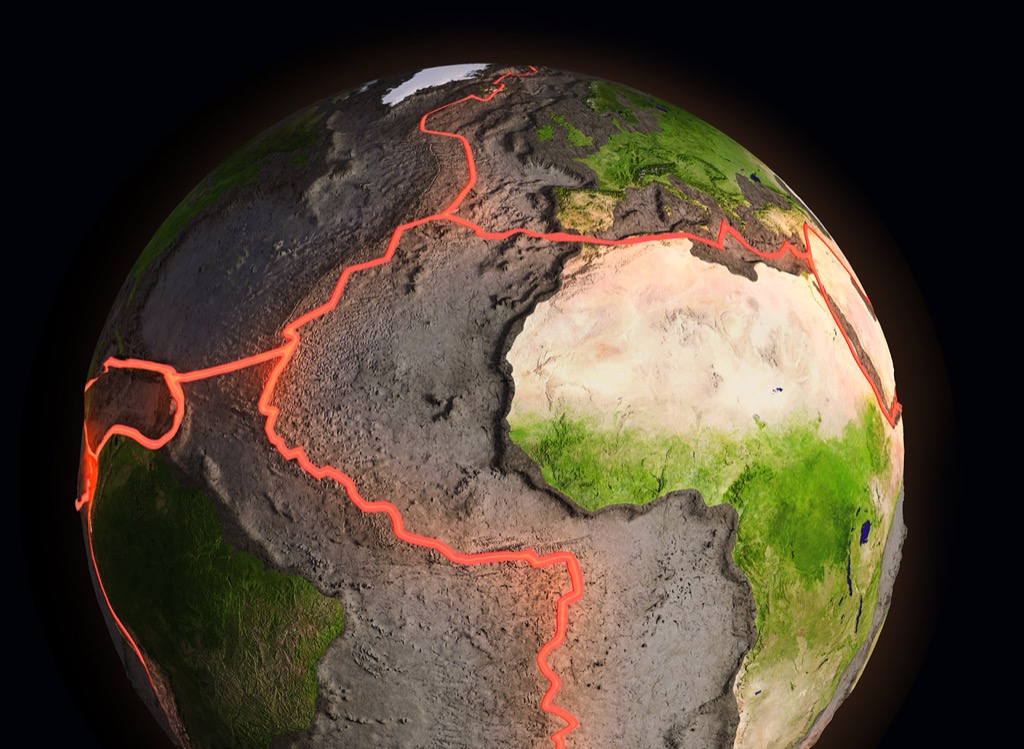
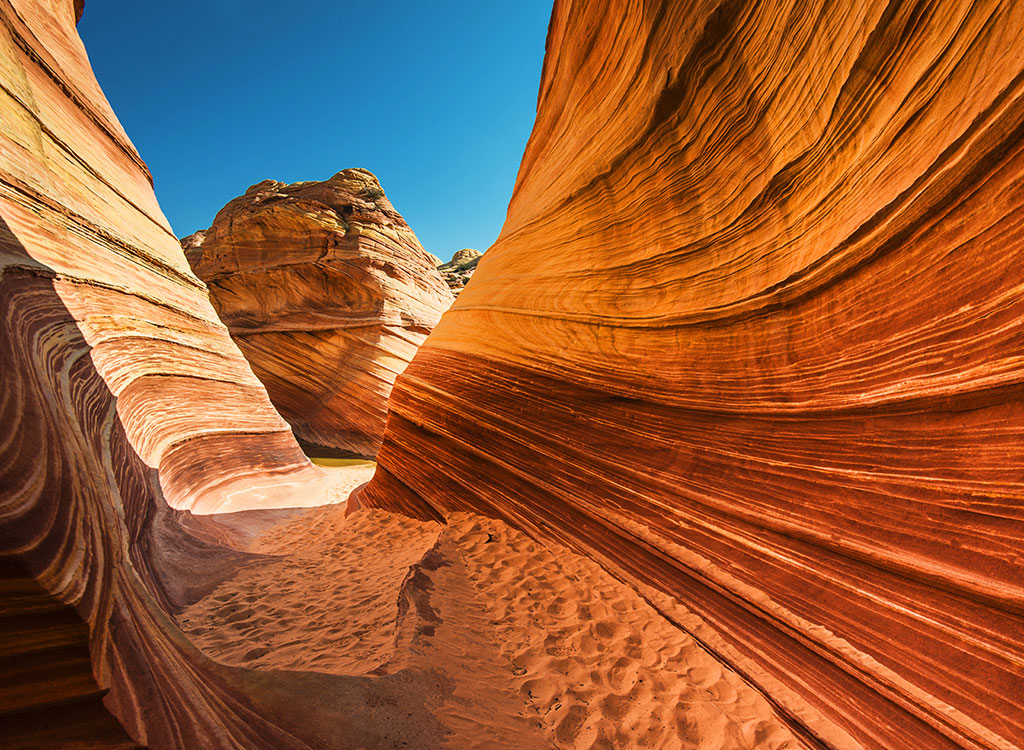



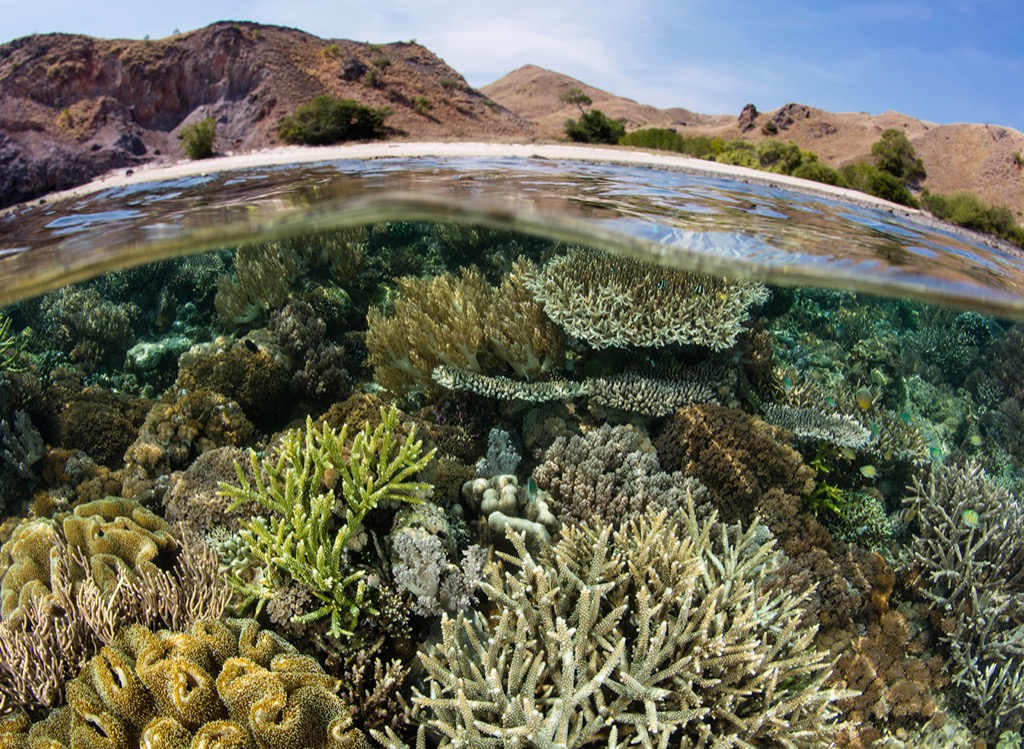
Ecosystems, Water and Land
Students can also learn about how living and nonliving components of an ecosystem plays a part in keeping the entire system functional and healthy; the stages of the water cycle and how it continually cycles around land, ocean and atmosphere; and visualize the various layers of the atmosphere.
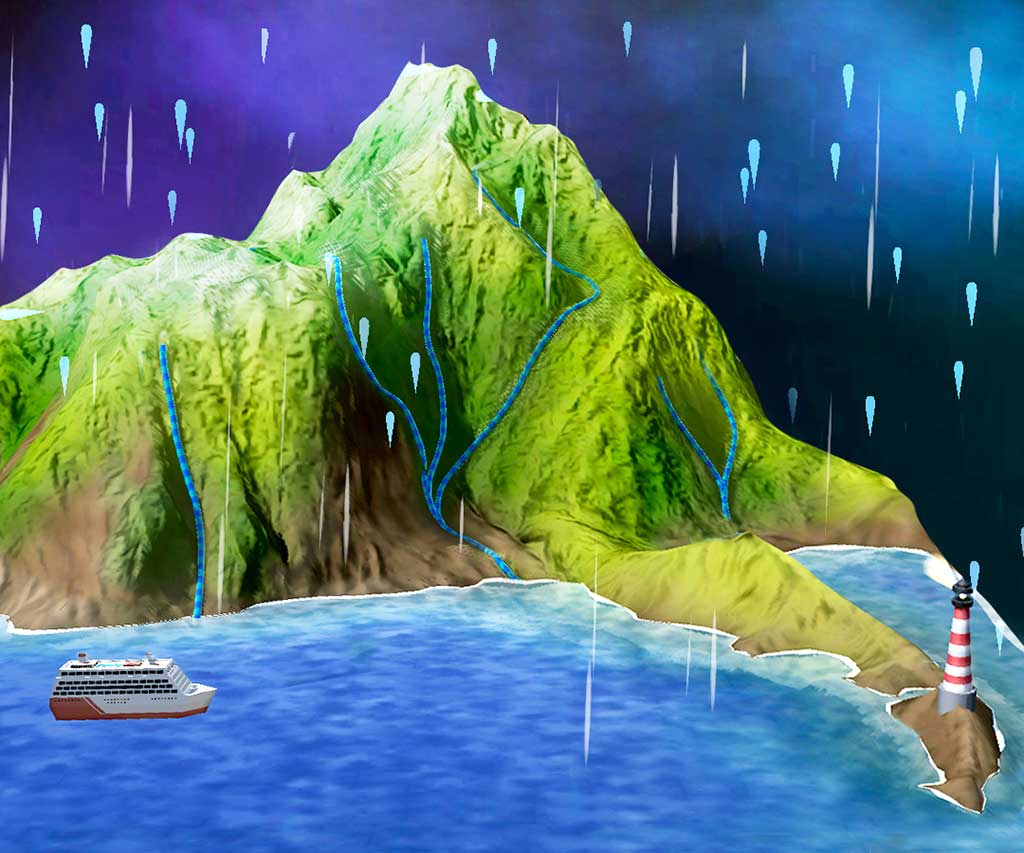





Renewable Resources
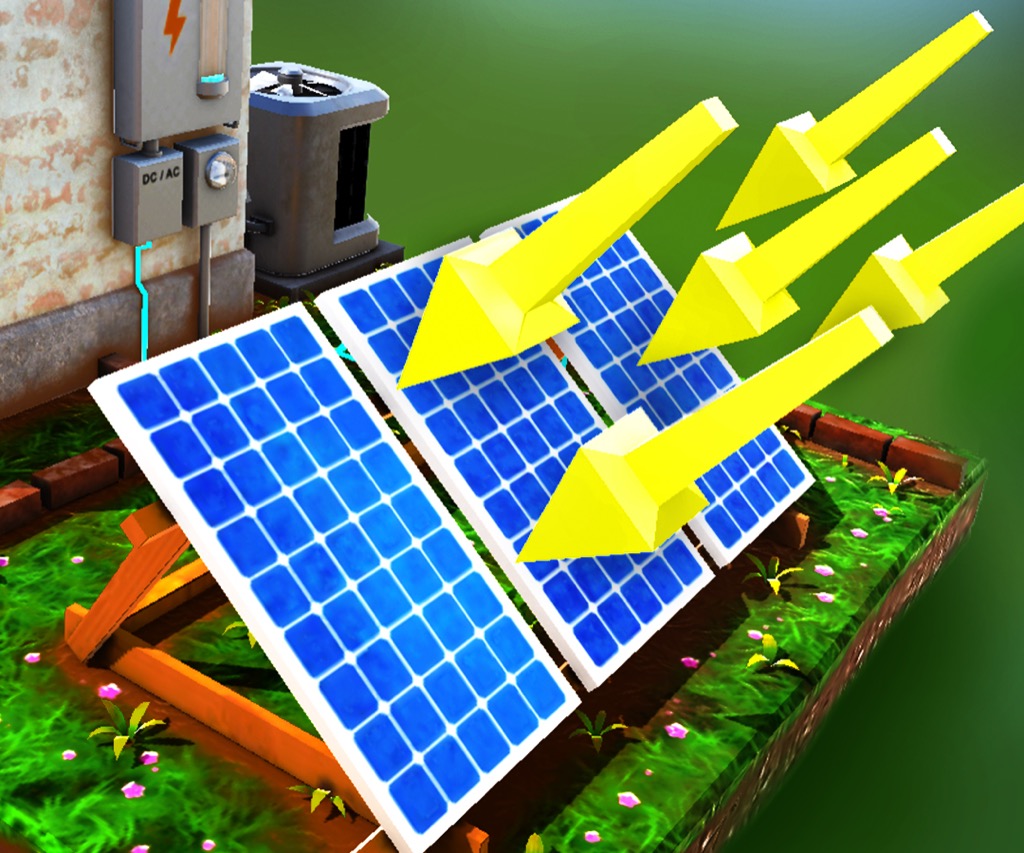
In addition to learning about the Earth and its processes on Earth Day, students can also take a look at various types of renewable energy which allows us to produce energy with very little waste or actual resource cost. The sun is important for this, but so are things like wind and water which also produce energy we can store and transport.


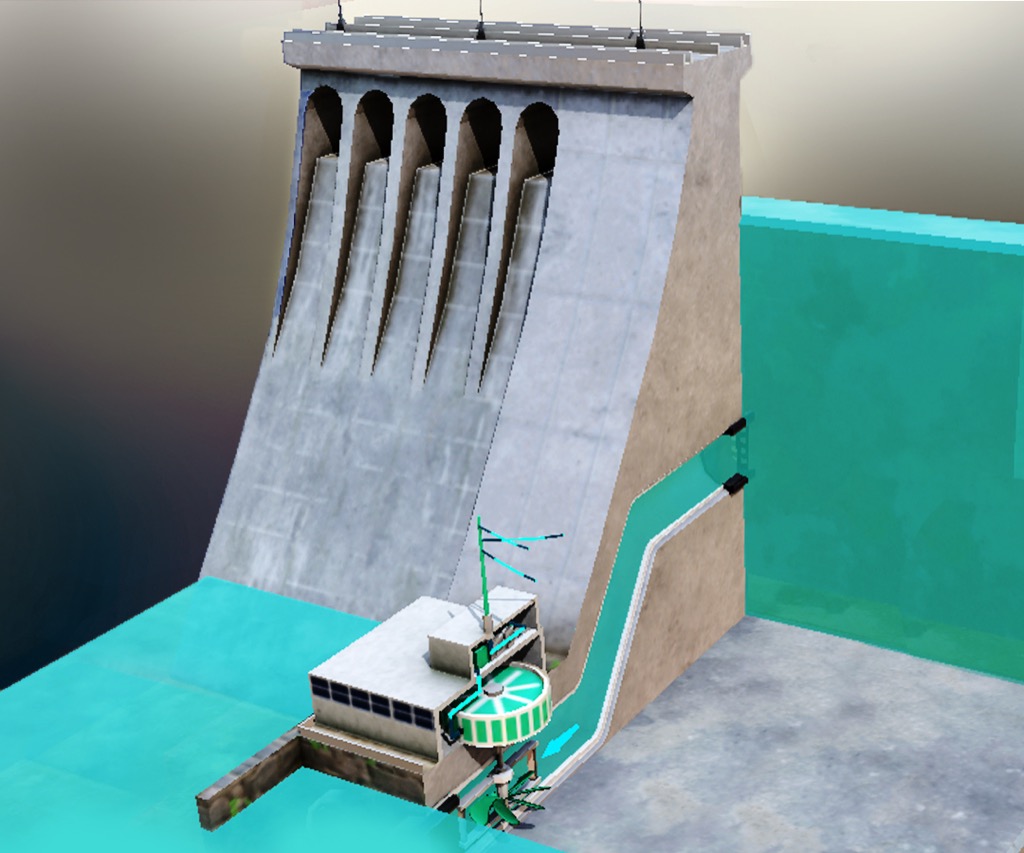
Not only will Merge EDU energize your Earth Day 2024 lesson plans, they'll foster an immersive, engaging, and dynamic learning environment where students can truly connect with our Earth's complex systems in a meaningful way. Happy Earth Day!!